Ⅰ. 서 론
EBT는 ICAO(International Civil Aviation Organization)의 “Doc 9995, Evidence Based Training(EBT)”을 기준으로 각 항공사의 상황에 맞게 수립하는 훈련프로그램으로 운항승무원 개개인의 역량 파악을 위하여 조종사에게 항공기의 기본 조작 및 비정상 상황을 부여하여 평가하는 방식이다. 이는 운항승무원의 전반적인 역량향상을 위해 각각의 항공사별로 발생하였던 운항품질보증(FOQA, Flight Operation Quality Assurance) 이벤트 또는 사고, 준사고 보고서 등의 증거(Evidence)를 기반으로 한 훈련프로그램을 개발 및 수립하여 운항승무원들의 역량을 평가하고, 이 결과를 바탕으로 운항승무원 개개인 별로 부족한 역량을 보완 및 훈련을 시행하는 것을 말한다.
국내 항공사는 EBT(Evidence Based Training) 프로그램을 개발하여 훈련 및 평가에 적용하고 있다. 2021년부터 대한항공과 티웨이항공은 훈련에 적용하여 실행 중이며, 타 항공사들은 훈련 모델을 개발 중에 있다. 현재 EBT 적용실태를 보면, EBT 모델에 대한 이해가 부족하여 훈련 성과를 이루지 못하는 현상이 발생하고 있다. 현재 적용된 국내 항공사의 EBT 훈련 모델은 분석과 실증 검증이 이루어지지 못해 조직의 목적에 부합한 훈련 목표를 달성하지 못하는 한계를 보인다. 따라서 본 연구는 EBT의 철학을 소개하고 이 훈련 모델이 달성하고자 하는 목표를 공고히 하는 데 목적이 있다. 이를 위해 EBT 훈련 모델개발에 있어 분석 중요성을 주목한다(최지헌, 2023).
EBT의 목적은 기존의 정량적(Quantitative) 기반의 훈련 방식과는 달리 항공기 운항 중에 예측하지 못한 비정상 상황 발생 시에 이를 적절하게 대처할 수 있 는 운항승무원의 역량(Competency)과 자신감(Confidence)을 향상하고, 비정상 상황을 극복할 수 있는 회복탄력성(Resilience)을 배양하고자 하는 데에 있다. 회복탄력성은 어려움이나 다른 어려운 상황에서 성공적으로 적응하고 긍정적으로 반응하는 개인의 능력으로 정의된다. 또한 운항승무원이 장애를 인식, 흡수, 및 반응하는 능력을 말한다(ICAO, 2010).
본 연구는 상기한 EBT의 목적에 부합하는 훈련프로그램 개발을 위하여 국내 항공사에서 발생한 FOQA 이벤트 중에서 하드랜딩(Hard Landing) 비행 데이터의 분석 결과를 통해 증거(Evidence) 기반의 실질적인 EBT 훈련프로그램을 개발하여 풍향, 풍속 요소에 따른 착륙 역량을 평가하고, 그 결과를 바탕으로 운항승무원 개개인 별로 부족한 착륙 역량을 보완하고 자신감을 함양하고자 한다.
Ⅱ. 본 론
역량(Competency)이란 ICAO에서는 Application of Procedure, Flight Path Management & Automation, Flight Path Management & Manual Control의 3가지 Technical Competency와 Communication, Leadership & Team Work, Problem Solving & Decision Making, Situation Awareness, Workload Management의 5가지 CRM (Crew Resource Management) Competency로 모두 8가지 Competency 항목을 제시하였고, 항공사는 이 8가지 역량을 발휘하는 데 필요한 구체적인 행동 방식인 Behavior Indicator(행동 지표)를 정하여 이에 따라 평가하고 있다(Table 1).
현재 항공사에서는 ICAO에서 제시한 역량(Competency) 발휘를 위해 필요한 구체적인 행동 방식인 Behavior Indicator(행동 지표)를 정하여 이에 따라 평가하고 있으며 이는 전통적인 훈련 방식과는 차이가 있다.
상기 Table 2에서와 같이 기존의 전통적인 훈련 방식이 운항승무원의 반복적인 조종 기술 및 절차수행 능력 향상이 목표였던 과거의 훈련 방식과는 달리 EBT 훈련프로그램은 실제로 항공기 운항 시 요구되는 전반적인 운항승무원의 역량향상을 목적으로 한다.
기존의 훈련프로그램이 정기 훈련 1일 차에 법적으로 요구되는 항목들에 대해서 훈련을 시행하고, 2일 차에 평가했던 과거의 방식과는 달리, EBT 훈련프로그램은 정기 훈련 1일 차에 운항승무원이 지난 정기 훈련을 마친 후에 일정 기간 라인에서 운항(Line Operation)을 하던 운항승무원의 기량 그대로의 평가를 통해 운항승무원의 비행안전 수준을 파악한다. 이러한 평가는 앞서 기술한 조종사의 8가지 역량(Competency)을 바탕으로 한 행동 지표(Behavior Indicator)에 의한 분석으로 이루어진다. 조종사는 각각의 개인적으로 부족했던 부분을 파악하게 되고, 비행안전을 위한 개선이 필요한 부분이 있다면, 이에 대해서는 정기 훈련 2일 차에 부족한 부분을 집중 훈련을 통하여 일정 기간 감소했던 개개인의 역량을 끌어올리는 것을 목표로 훈련프로그램이 구성되어 있다(Table 3).
| Grade | Five-stage |
|---|---|
| Grade 5 | Excellent |
| Grade 4 | Standard |
| Grade 3 | Acceptable |
| Grade 2 | Minimum acceptable |
| Grade 1 | Unacceptable |
EBT 훈련프로그램 평가(1일 차)는 각각의 항공사별로 설정된 기준에 따라 다르게 평가될 수 있다. 예를 들어 5단계의 평가(Grading)를 적용하고 있는 A 항공사는 5등급 중 4등급(Standard) 이상을 목표로 1일 차 평가 및 2일 차 훈련을 진행하고 있으며, 1일 차에 부족 역량을 보인 승무원들은 개인별 부족 역량에 따라 항공사의 훈련 목표인 4등급 이상을 달성하기 위해 보강훈련(Refinement Training)을 실시하게 된다.
EBT 훈련프로그램의 구성은 항공사마다 다소 차이가 있을 수 있으나, 기본적으로 항공사에서 발생하는 사고, 준사고, 이벤트들의 비행 데이터 분석 결과를 바탕으로 항공기의 사고 예방에 필요한 각 비행 단계별 훈련항목 및 주제를 선정하여 운영하고 있다.
항공사의 비행 데이터 분석 프로그램은 비행 데이터 모니터링(FDM, Flight Data Monitoring) 또는 운항 품질보증(FOQA, Flight Operational Quality Assurance)으로 알려졌다.
비행 데이터 분석 프로그램은 비행 중에 발생하는 이벤트 관련한 운항승무원의 조작 및 공항접근 절차, 환경적 요인, 항공기 비행 성능 등의 안전 운항의 경향성을 모니터링하여 표준 운항 절차(SOP, Standard Operating Procedure)에서 벗어나는 이벤트의 발생 원인을 식별하고 재발 방지 방안 마련 및 표준화를 유도한다. 또한 불안전한 위험 요인들을 사전에 제거함으로써 항공기의 사고 예방과 안전 운항을 확보하는 것을 목적으로 하고 있다(ICAO, 2014).
본 연구에서는 국내 A 항공사의 운항품질보증(FOQA) 프로그램에서 발췌된 B777 기종의 약 2년간 하드랜딩 24건을 대상으로 다음과 같이 분석하였다. 항공기의 수직 가속도(Vertical G)와 강하율(Descent Rate)의 상관관계, 저고도활공경사각(Low Vertical Path)의 이탈 정도(Glide Slope Deviation), 플레어 시의 바람 변화와 자세 변화의 데이터 분석을 통해 하드랜딩의 발생 원인을 규명하여 EBT 훈련프로그램 착륙단계의 훈련항목에 반영함으로써 하드랜딩의 사전 예방 안전 활동(Proactive and Precautionary Measures) 방안을 도출하고자 한다.
B777-200 항공기의 정상적인 착륙의 플레어(Flare) 시기는 지상으로부터 약 30ft 통과 시에 실시하며, 강하율(Descent Rate)이 접지 직전에 100fpm (Feet Per Minute) 이내로 감소되며 착륙이 이루어진다. 접근단계에서 강하율과 강하각의 연구에 의하면 접근속도 140KTS 이상, 3.5도 이상의 강하각에서 배풍을 받게 되면 강하율이 1,000fpm을 넘어가므로 각별한 주의가 필요하다(최지헌, 2023).
Fig. 1은 하드랜딩 편들의 접지로부터 0.5초 전 사이에서 발생한 항공기 최대 강하율과 Vertical G값을 비교한 것으로, 대부분의 항공기가 접지 직전까지 400fpm 이상의 높은 강하율을 유지하고 있는 것을 볼 수 있다(김현덕, 2020).
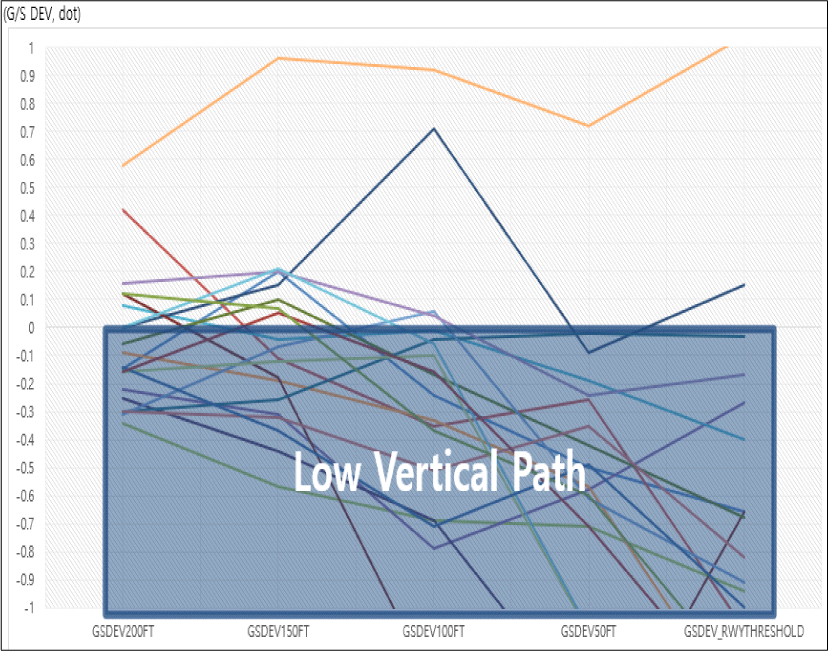
Fig. 2는 하드랜딩 이벤트 항공기들의 지상으로부터 200ft에서 활주로 Threshold 통과 시까지 50ft 단위로 G/S의 Deviation을 측정한 그래프이다. 세로축 가운데 0dot을 기준으로 파란색 네모 안의 Vertical Path가 200ft 이후 G/S Deviation Below 추세로 증가하는 것으로 나타난다. 200~100ft 사이에서 Below Path로 접근한 편들이 전체 하드랜딩 편의 77%를 차지하였다.
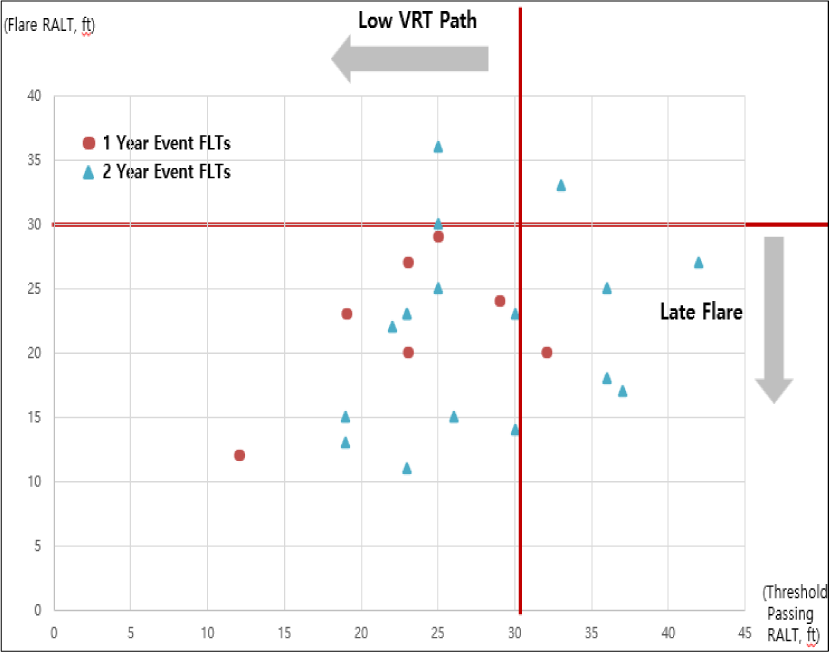
하드랜딩 이벤트의 활주로 threshold 통과 고도와 플레어(Flare)의 시작된 고도를 분석한 결과, 2편을 제외한 나머지 20건이 30ft 이하에서의 늦은 플레어(Late Flare)가 이루어졌다. 또한 정상적인 Threshold 통과 고도인 50ft보다 낮은 고도로 접근이 이루어졌다. 아울러 낮은 threshold 통과와 늦은 플레어(Late Flare)의 복합적인 요소가 함께 나타나는 경우도 많았다(Fig. 3).
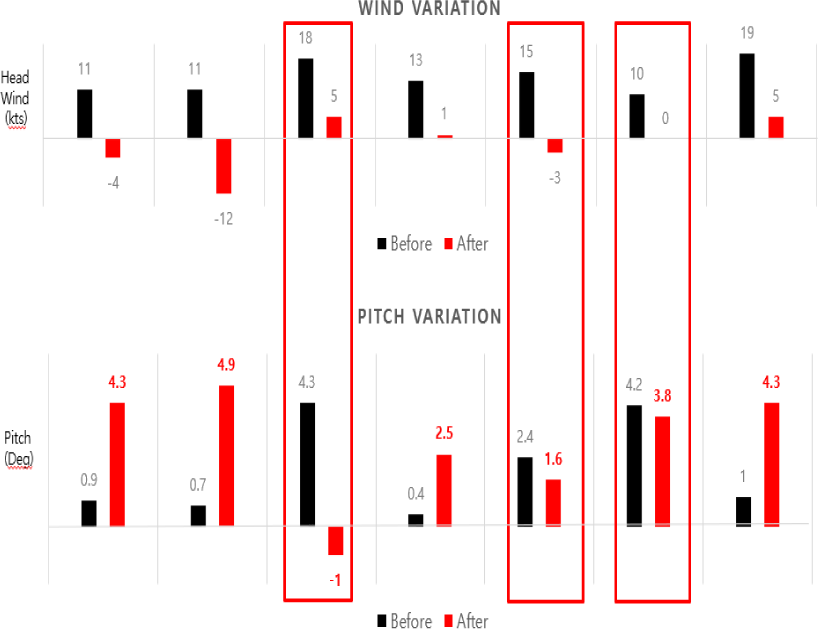
하드랜딩 건수 중에 50ft 미만에서 정풍 성분이 10kts 이상의 변화가 있었던 것은 총 7편이었으며, Fig. 4는 바람의 변화에 따른 플레어(Flare) 시의 기수(Pitch) 변화를 나타낸다.
정풍 성분의 감소로 인해, 항공기의 침하량이 많아져 급격하게 기수를 올리거나, 반대로 기수를 유지하지 못하고 기수를 내리는 경우가 총 3편이었다. 이 중 한편은 접지 순간의 바람 변화에 따라 기수를 4.3도까지 유지한 후 과도하게 기수를 내리는 과정에서 1.98G를 기록하였다.
Ⅲ. 결 론
국내의 항공사들이 ICAO 권고에 따라 새로운 교육훈련 프로그램인 EBT를 운영하고 있다.
EBT는 기존의 정량적인 훈련프로그램과는 다르게 운항승무원 개개인의 역량 파악을 위해 항공기의 기본 조작 및 비정상 상황을 부여하여 예측하지 못한 비정상 상황을 적절하게 대처할 수 있는 역량(Competency)와 자신감(Confidence)을 함양하는 새로운 훈련 방식이다.
또한 EBT는 각 항공사에서 발생하는 FOQA 이벤트 또는 사고, 준사고의 비행 데이터 분석을 증거(Evidence)로 하는 훈련프로그램을 개발하여 운항승무원 개개인 별로 부족한 역량을 보완하는 것을 목적으로 한다.
본 연구는 EBT 훈련프로그램의 목적에 부합하는 착륙단계의 훈련항목 및 주제 선정을 위한 비행 데이터 분석 프로그램(FOQA)의 활용방안을 도출하고자 B777 기종 24건의 하드랜딩(Hard Landing) 비행 데이터 경향성을 분석하였다. 분석 결과에 의하면 항공기가 접지 직전 200~100ft 사이에서 정상 접근경로 보다 낮은 접근경로(Below Vertical Path)로 접근한 편들이 전체 하드랜딩 편의 77%를 차지하였다. 아울러 운항승무원의 플레어(Flare) 시작 고도를 비교 분석한 결과, 대부분 30ft 이하의 고도에서 늦은 플레어(Late Flare)가 주요 발생 원인으로 식별되었다.
또한 하드랜딩(Hard Landing)의 원인으로 분석된 데이터 결과를 근거(Evidence)로 항공기가 정상적인 접근 각을 유지되지 못하는 원인으로 운항승무원(PF/ PM) 간의 인적요인(Human Factor) 측면까지 고려하였다. 기장과 부기장 간의 권력 거리(Power Distance)로 인한 동양적인 문화를 벗어나지 못하고 원만한 관계 유지를 위한 수동적인 PM(Pilot Monitoring)의 역할을 하나의 예로 들 수가 있다.
이러한 데이터 값을 근거로 하는 인적 요인(Human Factor)의 오류(Error)를 반영하는 EBT 훈련프로그램의 훈련항목을 구성한다면 개개인의 역량 강화가 목표인 EBT 훈련에서 추구하는 3가지 기량적 역량(Technical Competency)과 5가지 CRM(Crew Resource Management) 역량 강화의 목적을 시뮬레이터(Simulator) 훈련과목에서도 실제상황과 유사하게 달성할 수 있다. 또한 사례에 기반한 시나리오 훈련의 구성은 운항승무원이 비정상 상황에 대해 능동적으로 반응하고 해결하는 회복탄력성(Resilience) 배양을 도모할 수 있을 것이다.
이에 본 연구에서는 비행 데이터 분석을 활용한 EBT 훈련프로그램 하드랜딩 경감 훈련항목을 다음과 같이 제시하고자 한다. 첫째, PF(Pilot Flying) 조종사는 EBT의 Flight Path Management & Manual Control 역량(Competency)과 행동 지표(Behavior)를 함양하기 위하여 낮은 접근경로(Below Vertical Path)와 늦은 플레어(lAte Flare) 상황을 만들지 않도록 안정된 접근(Stabilized Approach)를 유지하는 것이 중요하며, 특히 200ft 이하의 고도에서 일정한 강하 경로(Vertical Path)의 유지를 재강조하는 시나리오 구성이 되어야 한다.
둘째, PM(Pilot Monitoring)은 안정된 접근(Stabilized Approach)의 범위(Criteria) 또는 SOP (Standard Operation Procedure)의 비행경로, 속도 및 강하율로부터 어떠한 이탈(Deviation)이 발생한다면, 반드시 적극적으로 콜아웃(Callout) 하여, Pf가 이를 수정하게 하거나 복행(Go-around)을 수행하게 하여 항공기가 비정상 하드랜딩 이벤트로 이어지는 것을 차단하여야 한다. 조종사는 착륙공항의 기상, 접근강하각, 공항 특이사항 등을 브리핑하고 PF, PM 임무수행을 FOM(Flight Operation Manual)에 명시하였다. 이러한 EBT 훈련프로그램을 통해 운항승무원은 Problem Solving & Decision Making의 역량이 함양되어야 한다.
연구의 한계점으로는 비행 데이터 분석 결과를 활용하는 EBT 훈련프로그램을 구성하기 위해서는 먼저 비행 데이터 분석 담당 부서의 신뢰성(Reliability) 있는 데이터의 수집이 선행되어야 하며, 비행 데이터 분석 결과와 관련된 교육훈련 및 인적요인(Human Factor), FOQA 분석팀 등의 부서 간의 긴밀한 협업과 그 결과에 대한 공유가 이루어져야 한다는 것이다.
또한 조종사가 고의로 SOP(Standard Operation Procedure)를 위반하거나 범죄적인 행위를 실행한 경우를 제외하고, 비행 데이터 분석 결과를 사용하여 조종사에게 인사상의 불이익을 주거나 해당 항공사를 처벌할 수 없는 비 처벌(Non-punishment) 정책이 보장되어야 비행 데이터 공유를 통한 EBT 훈련프로그램의 개발이 활성화될 것으로 판단된다.